Main Parts of Flower
Androcium and Gynoecium which are collective name of stamen and carpel.They are reproductive parts of flower.
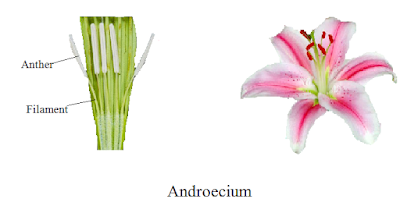
Andoecium It is collective name of stamens.It forms third whorl of flower.Stamen has two parts First part is Filament and second part is anther.Anther consist of anther lobes.These lobes are joined by a band convective chamber called pollen sacs.Pollen grains are produced in side the pollen sacs.The ripened anther burst and releases pollen grains. The side of anther containing connectives is called back and other side is called face.
Terms for Androcium
Different terms are used for androcium. The terms which are used for androcium are.
Polyandrous:The stamen are free from each other. These stamen may be di, tri and tetra or petandrous. Stamens are present in different numbers in it.
Didynamous: Stamens are four four in number. Four of these stamen two is short and two is long.All is present in single whorl .Example of didynamous is ocium. All stamen are free form each other. Tetradynamous: Stamens are six in number.Four long and two is short. Example is Brassica, Radish Epipetalous: The term in which stamen fused with petal.It is present in in fused.Its example is potato
Antipetalous: Stamens are opposite to petals .Stamen present on opposite side of petals.Example zizyphys. Antiseplous: Stamens are opposite to the sepal. Gynandrous: Stamens are fused with the gynocium. Adelphous: Stamens are united by their filament. It may be monocotyledonous, diadelphous or polyadelphous. Example Cirus, castor oil.
Attachment anther on filament
Anther are attach with filament. In the anther pollen grain are produced. In is part of male reproductive organ.It is present on the tip. There are four type of attachment of filament to anther. Basfixed or Innate: The filament is is attach to the base of anther. It example is Brassica.
Adnate: In this case no joint is present between the filament and the base of anther. Filament runs along the whole length of the anther from base to apex. Example of adnate is butter cup.
Dorsifixed: Filament is attached to the back of anther.The anther become immovable.Example Passion.Versatile: Filament is attached to the back of anther. It can swing on it.Example is grass.
Gyonecium or pistil
Gynoecium forms fourth whorl of the flower.It occupies the center of the thalamus. It may consist of one or more carpel. These carpel may be remain free or combined. Or they fuse to form compound pistils. Each carpel has three parts Ovary, Style and Stigma.
Ovary It is basal swollen portion of the carpel. It enclose one or more chamber or loculi. The chamber has one and ovules.It is main part of the carpel. It is present near the anther on the flower.
Style Slender and stalk structure. It arise from top of ovary. It contain styler tissues.Sometime hallow. Stigma It is top of the style. It receive the pollen grain which are come form the pollentube.
Style Slender and stalk structure. It arise from top of ovary. It contain styler tissues.Sometime hallow. Stigma It is top of the style. It receive the pollen grain which are come form the pollentube.
Evolution of Carpel
It believed that carpel is modified leaf. The leaf is folded. Its two edges are fused and meet together. This line of union is called ventral structure. The opposite side is called dorsal structure. The borad lower portion of the folded leaf forms ovary. The elongated apex from style. The style is swells slightly to form stigma. Placenta develop along the ventral structure on the inner surface of wall of the ovary. Ovules are attached to the placenta is two rows.
Descriptive terms In the gynoecium different are used for it. Some of these terms are Monocarpellary Gynoecium consists of single carpel. Example is pea. They have only one carpel. Biscarpellary The gynoecium consists of two carpel. These carpel may be free or fused. Example potato. Polycarpillary Gynoecium has more than one free carpel. Example of pollycarpillary is Butter cup. Apocarpous.
The cushion like ridges inside the ovary on which ovule are attached is called placenta. Arrangement of placentas in the ovary is called placentation. They have special arrangment of it. Their arrangment have different cases. In some cases placenta is formed along fused margins of ovary. The gynoecium is monocarpellary or polycarpillary and apocarpous. Example is Cassia and etc In the other cases ovary is compound and uni ocular. The fused margins of the carpel swell up to form placentas. Ovules attach on it. Sometime fused margins of the carpel grow inward to form incomplete septa. It divides each ovary into number of incomplete compartments. The ovules are borne on the surface of septa like chamber. The chamber was given its number.
In Brassica the placentation is partial. It has bicarpellary ovary. This compound ovary become bicoular due to the formation of false septum. Some of these cases gynoecium is polycarpillary and syncarpous. The fused margins of carpels grow inward in the center of ovary. The marginal placenta of all the carpels fuses in the center to form a central axis.Ovules are attached on this central axis .Example of this case is Potato Eu phobia. Sometime a number of fall septa is formed on it.


0 comments:
Post a Comment